A Comprehensive Platform for Multi-species Long Non-Coding RNA Peptide Atlas
Introduction
Here, we designed the LncPepAtlas database, which aims to construct an integrated annotation platform for the upstream regulation of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and to develop a resource that compiles various translational evidence for lncRNA encoded peptides across multiple species.
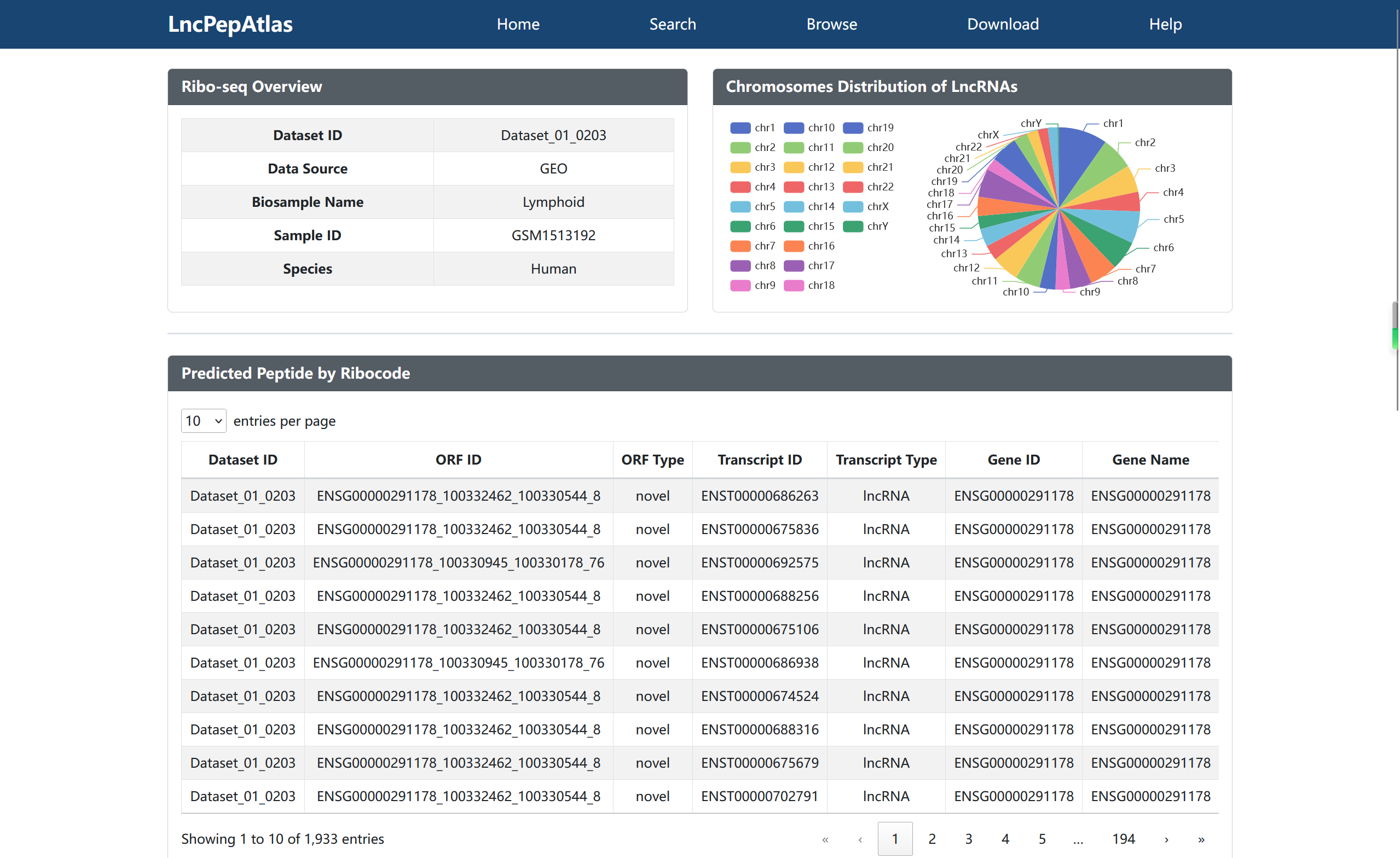
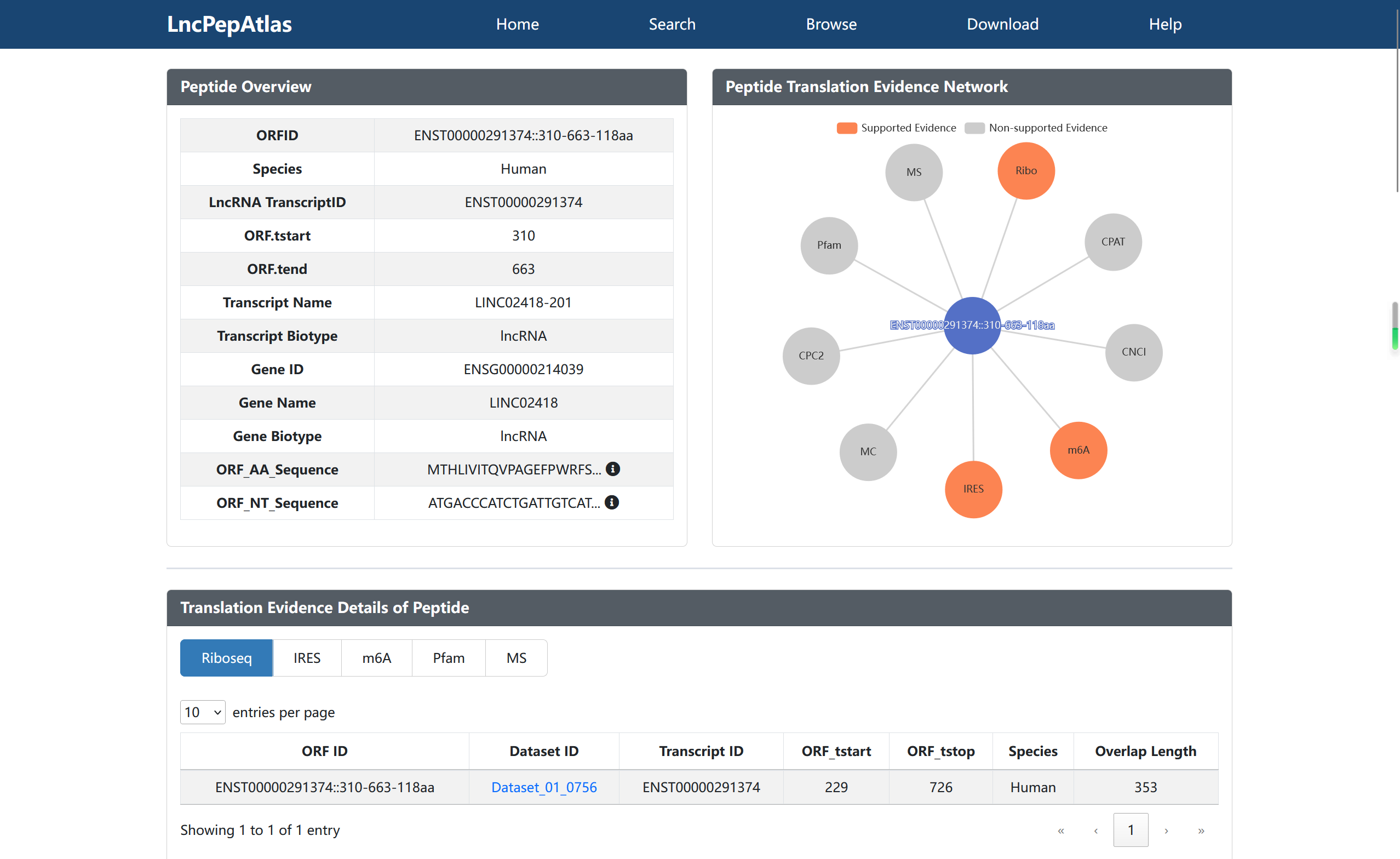
The current version of LncPepAtlas collects and analysis 2,655 ribosome profiling datasets from nine species, including human, mouse, rat, arabidopsis, c.elegans, zebrafish, fruitfly, yeast and e.coli. Then, nine methods were employed to assess the translational evidence of lncRNAs derived from the Ensembl database, including manual curation, ribosome occupancy, IRES, m6A, mass spectrometry, Pfam, CPC2, CPAT, and CNCI. In addition, LncPepAtlas supports multiple types on upstream regulation annotation of these lncRNAs, such as transcription factors (TFs), super-enhancers (SEs), enhancers, silencers and accessible chromatin. As well as lncRNA expression annotations across a diverse range of cancer types, tissues or cell lines. In particular, LncPepAtlas provides users with all possible small peptides encoded by lncRNAs and performs protein domain annotation, neoantigen potential analysis and homologous sequence alignment analysis for these small peptides to predict the function of small peptides.
LncPepAtlas provides a user-friendly interface for searching, browsing and downloading lncRNA and small protein related information.We believe LncPepAtlas will become a useful and effective platform for exploring the potential functions and regulations of translatable lncRNAs and their encoded small peptides in diseases and biological processes.
Data Statistical Table
| LncRNA | The Number of Sources | 1 |
| The Number of Species | 9 | |
| Ribo-seq | The Number of Sources | 4 |
| The Number of Species | 9 | |
| The Number of Samples | 2631 | |
| TF(ChIP-seq) | The Number of Sources | 5 |
| The Number of TFs | 1043 | |
| The Number of Samples | 11056 | |
| Super-enhancer | The Number of Sources | 4 |
| Enhancer | The Number of Sources | 7 |
| ATAC-seq | The Number of Sources | 1 |
| Silencer | The Number of Sources | 1 |